As societal norms evolve and women increasingly delay childbirth, the concept of geriatric pregnancy has become a prominent topic. This article delves into the specific age considerations surrounding geriatric pregnancy, exploring the risks associated with conceiving at an advanced maternal age and providing insights to empower women making decisions about their reproductive health.
Defining Geriatric Pregnancy by Age
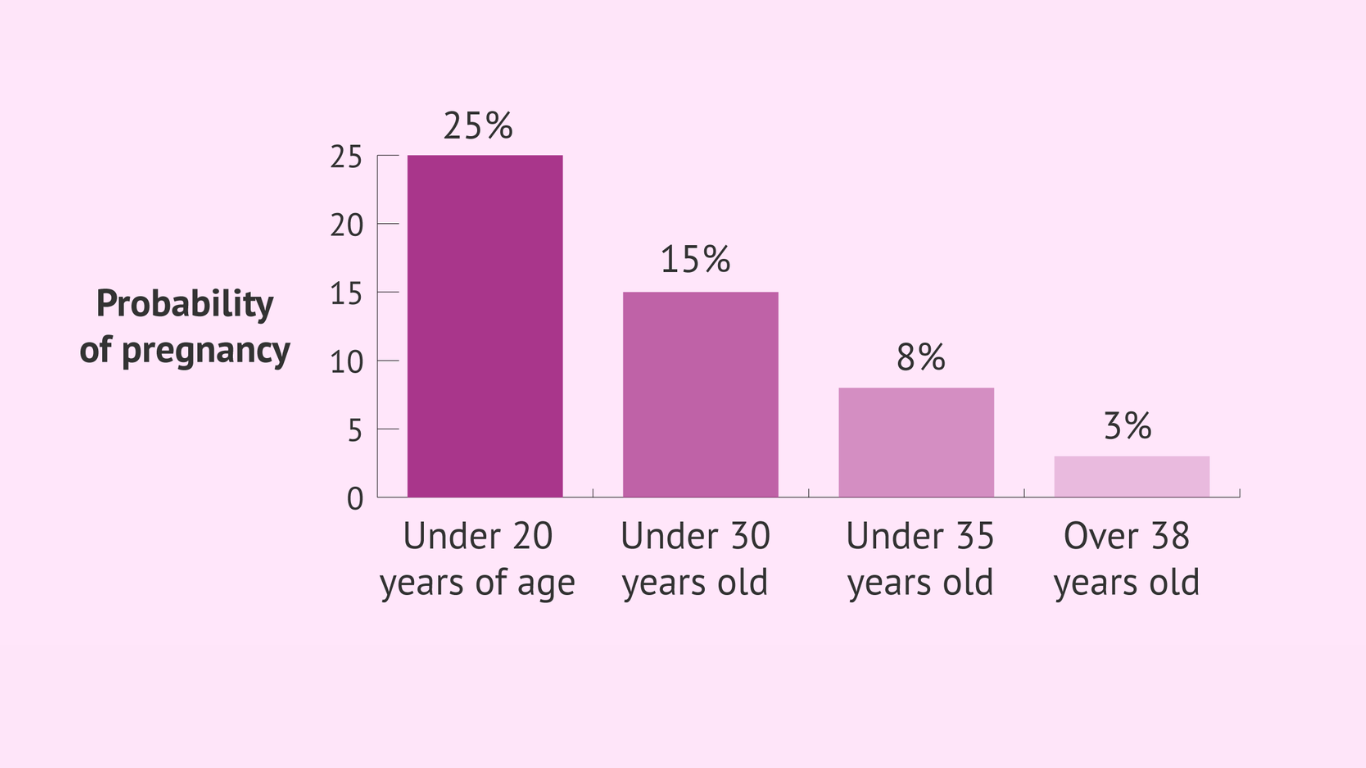
Geriatric pregnancy, often clinically termed as Advanced Maternal Age (AMA), refers to pregnancies in women who are 35 years old or older. This categorization is not a judgment on a woman’s health but a recognition of the unique challenges and considerations that come with pregnancies in this age group.
The Changing Landscape of Pregnancy Age
In recent decades, there has been a notable shift in the age at which women choose to start families. Various factors contribute to this trend, including career pursuits, financial stability, and changing societal expectations. As a result, more women are navigating the journey of pregnancy in their late 30s and beyond.
Risks Associated with Advanced Maternal Age
1. Chromosomal Abnormalities
One of the primary concerns in geriatric pregnancy is the increased risk of chromosomal abnormalities, such as Down syndrome. Advanced maternal age is associated with a higher likelihood of genetic anomalies, necessitating specialized screening and diagnostic tests.
2. Pregnancy-Related Conditions
Women in the geriatric pregnancy age range may face a higher incidence of pregnancy-related conditions, including gestational diabetes, hypertension, and pre-eclampsia. Close monitoring and proactive management are crucial to ensure the well-being of both the mother and the baby.
3. Fertility Challenges
While fertility varies among individuals, women over 35 may experience challenges in conceiving. The natural decline in fertility with age underscores the importance of early family planning for those considering pregnancy in their late 30s or beyond.
learn more: Golden Wombs – Embracing the Miracle of Late-in-Life Motherhood
Empowering Women in the Decision-Making Process

1. Education and Awareness
Empowering women begins with education and awareness. Understanding the potential risks associated with geriatric pregnancy allows women to make informed decisions about the timing of their pregnancies.
2. Prenatal Counseling
Early prenatal counseling is key for women contemplating pregnancy in their late 30s or beyond. This includes discussions about fertility, genetic testing options, and proactive measures to mitigate potential risks.
3. Supportive Healthcare
Access to supportive and empathetic healthcare is crucial for women navigating geriatric pregnancies. A healthcare team specializing in maternal-fetal medicine can provide comprehensive care and guidance tailored to the unique needs of older expectant mothers.
Geriatric pregnancy, defined by age, presents distinct challenges and considerations. However, with the right information, proactive healthcare, and a supportive community, women can confidently navigate this unique journey. Age should not be a deterrent to motherhood but rather a factor to be mindful of when planning and managing a pregnancy.
As the landscape of pregnancy continues to evolve, embracing the diversity of reproductive journeys empowers women to make choices aligned with their individual circumstances and aspirations. Through education, support, and personalized healthcare, geriatric pregnancy can be a fulfilling and healthy experience for women choosing to embrace motherhood later in life.
learn more: Silver Bumps – A Comprehensive Guide to Pregnancy After 35