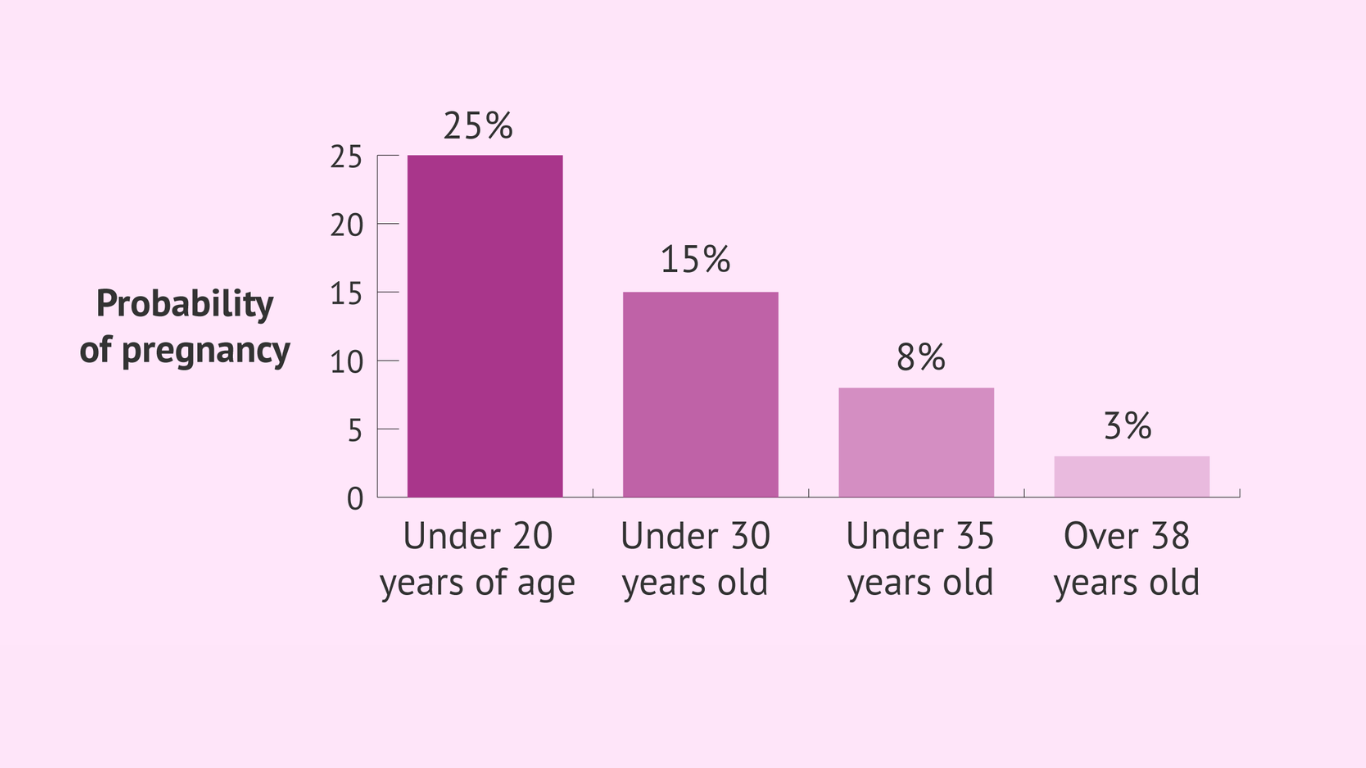
Pregnancy is a transformational and joyful event, but for women who conceive later in life, there are typically additional considerations and risks. Advanced maternal age, which is defined as pregnancy after the age of 35, might create complications that must be carefully managed. This article is a thorough guide for older mothers, including insights on assessing, minimizing, and managing pregnancy risks for a healthy and rewarding road to motherhood.
Understanding Risks Associated with Advanced Maternal Age:
Fertility Considerations:
- Myth vs Reality: Dispelling the notion that conception is impossible for older mothers and exploring fertility preservation options.
- Medical Interventions: Understanding assisted reproductive technologies, such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) and intrauterine insemination (IUI), as viable options.
Pregnancy Complications:
- Common Concerns: Addressing heightened risks for conditions like gestational diabetes, hypertension, and preeclampsia.
- Regular Monitoring: The importance of frequent prenatal check-ups and diagnostic tests to detect and manage potential complications early on.
Genetic and Chromosomal Abnormalities:
- Increased Risk: Acknowledging the higher likelihood of genetic disorders, such as Down syndrome, and the importance of genetic counseling.
- Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT): Exploring advanced screening options for early detection and informed decision-making.
Mitigating Risks through Lifestyle and Healthcare:
Nutrition and Exercise:

- Balanced Diet: Emphasizing the role of a nutritious diet in promoting maternal and fetal health.
- Safe Exercise: Encouraging appropriate physical activity to manage weight and reduce the risk of gestational complications.
Prenatal Care:
- Timely Check-ups: Stressing the significance of regular prenatal visits for continuous monitoring of both maternal and fetal well-being.
- Individualized Care Plans: Tailoring healthcare strategies to each mother’s specific needs and medical history.
Emotional and Mental Well-being:
- Support Networks: Recognizing the importance of a strong support system during pregnancy, especially for older mothers.
- Mental Health Resources: Accessing counseling and mental health services to navigate the emotional aspects of pregnancy.
Empowering Older Mothers for a Positive Pregnancy Experience:
Educational Resources:
- Informed Decision-Making: Providing reliable information to help mothers make educated choices about their pregnancy journey.
- Anticipating Challenges: Understanding potential hurdles and preparing emotionally for the unique aspects of later motherhood.
Community Engagement:
- Connecting with Peers: Encouraging older mothers to join support groups or online communities for shared experiences and advice.
- Celebrating Diversity: Embracing the diversity of family structures and breaking societal stereotypes around maternal age.
Managing pregnancy risks for older women requires a combination of education, proactive care, and emotional support. By debunking stereotypes, acknowledging particular challenges, and taking a holistic approach to well-being, older women can embark on a journey to parenting that is not only healthy, but also empowering and rewarding. This guide is an invaluable resource for negotiating the complications of pregnancy in later life, resulting in great outcomes for both moms and their darling bundles of joy.