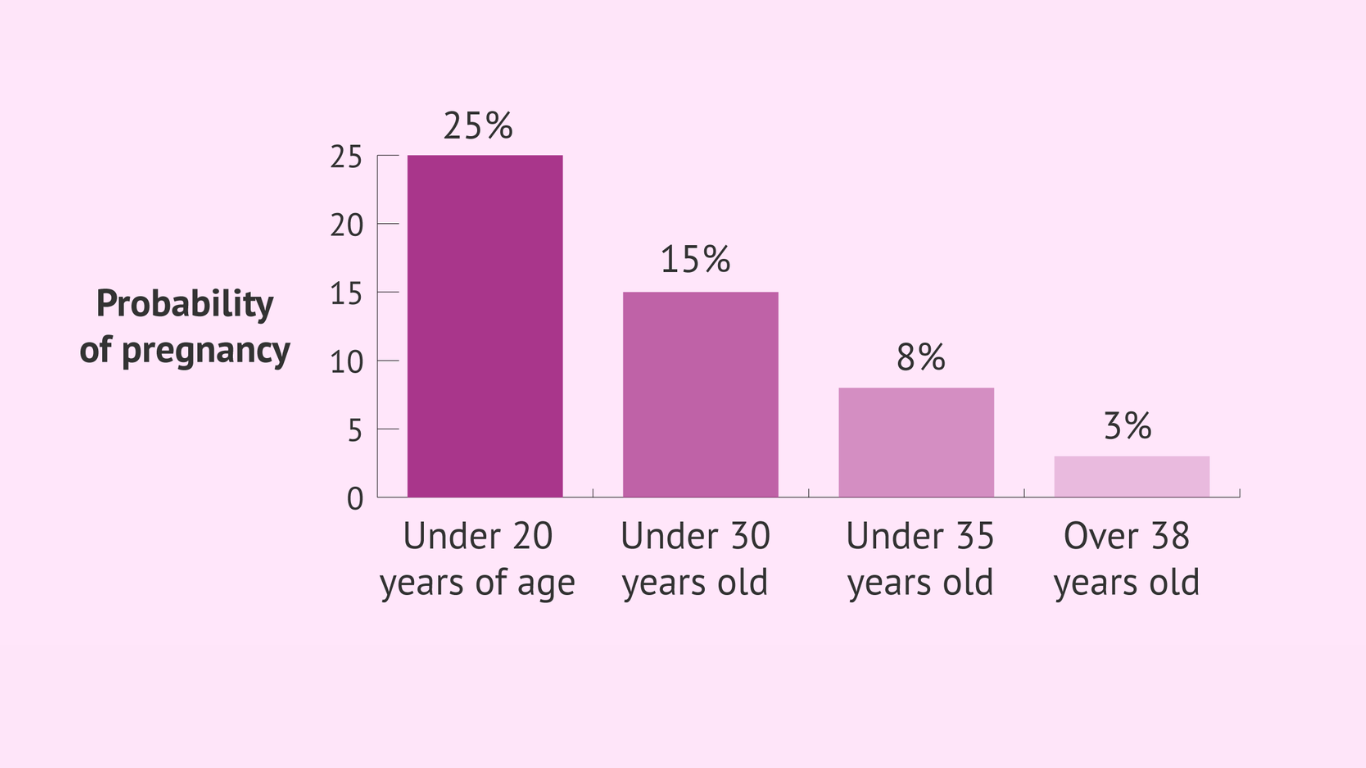
In order to ensure women’s safety and well-being, maternal health care must be provided from the time of conception until the time of delivery and the postpartum period.
Maternal health care addresses the physical, mental, emotional, and social aspects of a woman’s health in order to make her pregnancy and delivery a positive experience. It also ensures that the mother and child are safe and well-cared for, taking precautions to avoid any risks or complications. The mother throughout her pregnancy, labor, and recovery.
Learn about the procedures for women’s prenatal care in this article, as well as how to look after a mother’s health both during and after childbirth.
Early prenatal care for mother’s health
Pregnancy care aids in preventing any issues, preparing for a healthy pregnancy, and producing a healthy child. The best time to start care is three months or more before trying to get pregnant. It should be mentioned that different women may need different amounts of time to prepare physically and mentally for pregnancy.
Planning a pregnancy starts with a consultation with your physician or health center for preconception care. The following are some of the most crucial things to think about and talk about with the doctor:
- Health and family history: It’s advisable to let your doctor know about any illnesses in your family members, as certain diseases, such sickle cell anemia, are hereditary and can have an impact on the fetus’s development. Not only that, but we’ll go over how to prevent any difficulties from the past pregnancy, such heavy bleeding, repeated miscarriages, or birth defects.
- Health issues: Before getting pregnant, it’s critical to manage any pre-existing conditions, including diabetes, thyroid illness, high blood pressure, gum and tooth disease, and STDs.
- Medication: When a woman is planning a pregnancy, you should inform her doctor about all of the medications, nutritional supplements, and herbal remedies she takes. She should also see a doctor before taking any medications during her pregnancy as some medications can cause serious birth defects.
- Lifestyle and surroundings: Talk about some regular daily routines that could have an impact on the mother’s and the fetus’s health, including drinking alcohol or smoking. Exposure to these substances can result in major complications like birth deformities, premature birth, or fetal death, in addition to harmful compounds and environmental pollutants like fertilizers, pesticides, and cat excrement that should be avoided.
- Vitamins: A few vitamins should be taken at dosages prescribed by a physician both before and throughout pregnancy. Folic acid is the most crucial vitamin since it helps prevent birth abnormalities of the spine in the developing child.
- Mental health: Pregnant women can experience anxiety and fear, therefore it’s critical that the pregnant mother receives moral and social support from her spouse and family, as well as other forms of support. It is also possible to talk about all the suitable choices for treating any psychological issues that call for therapy intervention during pregnancy.
maternity care during the maternity period
After conception, it’s critical to keep an eye on the mother’s physical and mental well-being throughout the nine months of pregnancy in order to preserve both her and the fetus’ safety and to promptly address any medical emergencies. This is usually accomplished by following the regular doctor’s appointment schedule, which looks something like this:
- For the first six months of the pregnancy, a monthly visit.
- During the seventh and eighth months of pregnancy, schedule a visit every two weeks.
- During the ninth month of pregnancy, a weekly visit.
The doctor checks on the pregnant woman on a regular basis to monitor the fetus’s progress, the mother’s health, and the possibility of any pregnancy-related complications or issues. Some of the tests the doctor may perform during these visits are as follows:
- A pelvic exam is performed to measure the uterus’s dimensions and form.
- Test for anemia via blood.
- Check your body’s iron levels.
- tests for hepatitis and other infectious illnesses.
- After the twentieth week, take the uterus’ height.
- Examine your blood sugar levels to rule out gestational diabetes.
- measuring the height of protein, as this may indicate preeclampsia.
- Fetal heart rate is measured via ultrasound imaging to track the development of the fetus.
- Tests such as blood work or any other necessary diagnostics to keep an eye on a chronic illness the mother had before becoming pregnant.
In addition, the doctor assists the pregnant woman in managing or curing common pregnancy symptoms like insomnia, back discomfort, and morning sickness. Not to mention assisting her with the following
Weight
While gaining excess weight during pregnancy can lead to health issues and challenges that impact both the expectant mother and the fetus, it can also assist the fetus grow and thrive.
- diabetes throughout pregnancy.
- In the future, developing type II diabetes.
- elevated blood pressure.
- The labor and delivery procedure is more challenging.
- Having trouble shedding extra pounds after giving delivery.
- higher chance of obesity in the offspring or mother in the future.
However, attempting to shed even a small amount of weight while pregnant may have an adverse effect on the health of the mother and fetus, so you should consult your doctor about your weight.
Nutrition
One aspect of caring for the health of the expectant mother is taking care of her nutrition, as the need for vitamins and minerals, such as folic acid and calcium, increases during pregnancy. There are also some types of foods that are recommended to eat during pregnancy and others that are recommended to be avoided.
Foods recommended to eat during pregnancy
Foods that provide many vitamins and minerals to pregnant women include:
Fruits and vegetables.
Whole grains, such as oatmeal.
Skimmed or low-fat milk and dairy products.
Protein from healthy sources, such as beans and lean meats.
Read more: The perfect food for pregnant women
Foods recommended to avoid during pregnancy
There are certain foods that may harm the health of the mother and fetus during pregnancy, such as:
Caffeine, and it is recommended to drink decaffeinated coffee or tea or reduce caffeine intake to less than 200 mg per day.
Fish and seafood containing high levels of mercury.
Unpasteurized cheeses, undercooked meats, can cause transmission of some types of parasites and bacteria.
Alcohol.
It is worth noting that some women may crave clay, ash, or other things that are not considered food, and this may be an indication of a lack of some nutrients in pregnant women, and it is recommended to consult a doctor if you suffer from this.
Physical activity
preserving physical activity during pregnancy is a vital aspect in preserving and caring for the mother’s health, and unless there is a medical contraindication, engaging in specific physical activities provides different benefits for pregnant women, such as:
Gain weight in an appropriate amount.
- Reduce your back pain and bloating.
- Lower the risk of gestational diabetes.
- Decrease the risk of postpartum depression.
- Shorten the length of labor and make delivery easier.
- Minimize the time needed to recover after delivery.
Examples of some physical activities that are generally considered safe during pregnancy include walking, yoga, and swimming.