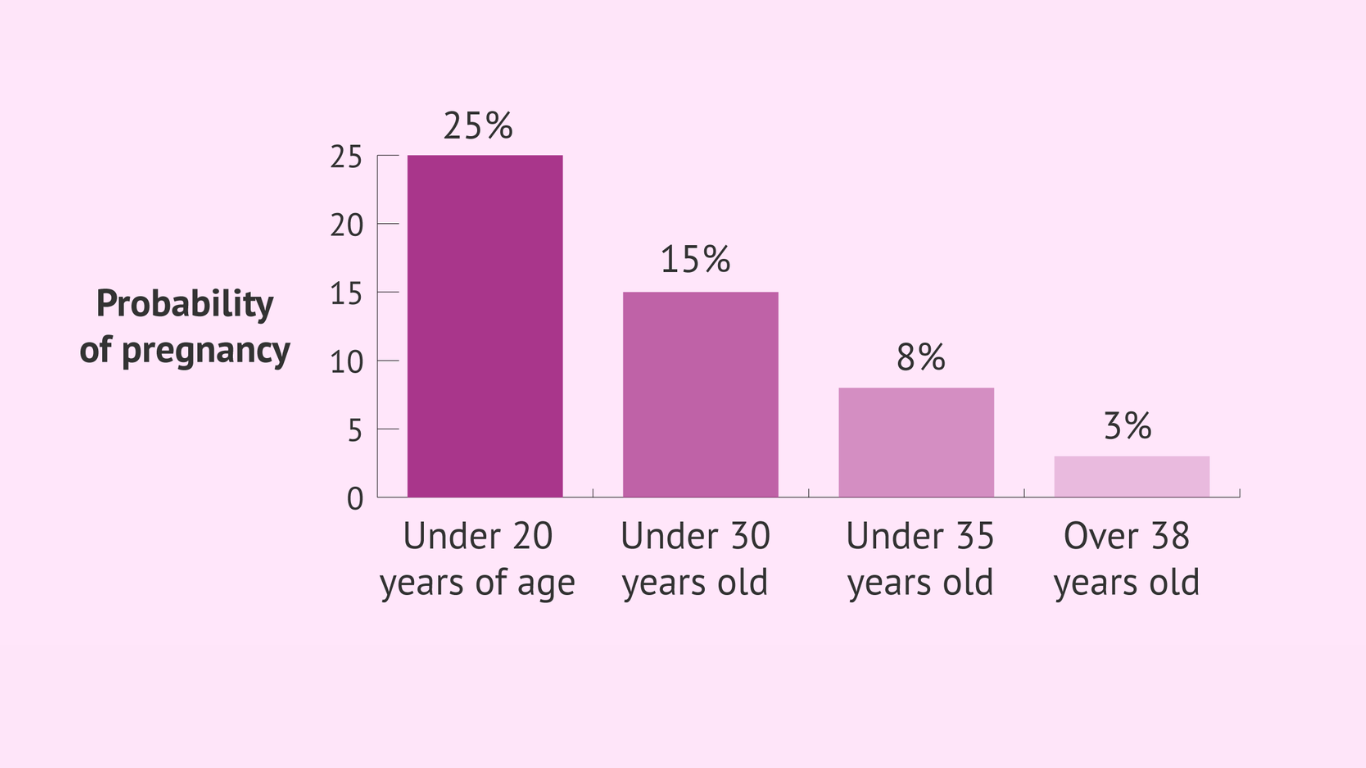
Advanced maternal age, generally defined as pregnancy occurring in women aged 35 years and older, has become increasingly common in contemporary society. While many women today choose to delay childbirth for various reasons, it is essential to explore the potential impact of advanced maternal age on both maternal and neonatal outcomes.
Maternal Outcomes:
Increased Risk of Pregnancy Complications:
- Advanced maternal age is associated with a higher risk of pregnancy complications such as gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, and placenta previa. Understanding these risks is crucial for appropriate antenatal care.
Cesarean Section Rates:
- Studies suggest that older mothers are more likely to undergo cesarean sections. This could be attributed to factors like an increased prevalence of medical conditions or concerns about fetal well-being.
Maternal Health:
- Advanced maternal age may contribute to an increased prevalence of pre-existing health conditions, such as hypertension and diabetes, which can complicate pregnancy and necessitate careful management.
Neonatal Outcomes:
Preterm Birth and Low Birth Weight:
- A greater chance of preterm birth and low birth weight is linked to older mothers. This could be connected to the rise in several pregnancy-related problems.
Congenital Anomalies:
- Research suggests a correlation between advanced maternal age and an elevated risk of congenital anomalies. However, the absolute risk remains relatively low, and prenatal screening can aid in early detection.
Neonatal Mortality:
- While the majority of babies born to older mothers are healthy, there is a slightly higher risk of neonatal mortality. Pregnancy problems and underlying medical disorders frequently impact this risk.
Psychosocial Factors:
Parenting Challenges:
- Advanced maternal age may bring unique parenting challenges, including increased stress and potential health issues for older parents. Exploring these psychosocial aspects is crucial for comprehensive understanding.
Fertility Treatments:
- Older mothers may resort to fertility treatments, which can impact both maternal and neonatal outcomes. Examining the effects of assisted reproductive technologies is essential in this context.
While advanced maternal age can pose certain risks, it’s crucial to note that many women in this age group have healthy pregnancies and deliver healthy babies. The impact of advanced maternal age on maternal and neonatal outcomes is multifaceted and influenced by various factors. Adequate prenatal care, early intervention, and addressing specific risk factors can contribute to positive outcomes for both mothers and newborns. As societal trends continue to shift, ongoing research is necessary to refine our understanding of the complexities surrounding pregnancy at an advanced maternal age.