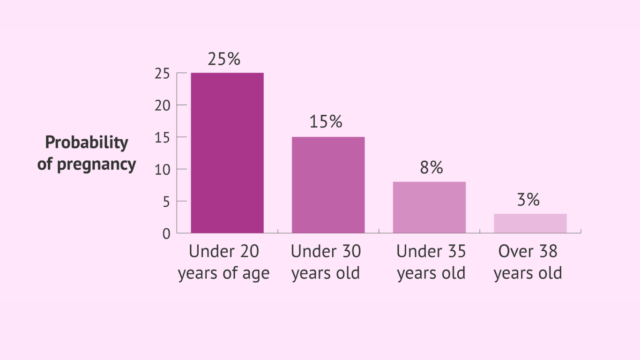
Pregnancy is a transforming journey that involves multiple physical and emotional changes, and older mothers may face special problems. Advanced maternal age, which is typically defined as pregnancy at or after the age of 35, offers its own set of concerns and health risks. Strategic use of prenatal vitamins is an important part of prenatal treatment for older women. In this comprehensive guide, we look at the importance of prenatal supplements for older mothers, including their advantages, suggested nutrients, and the impact on maternal and fetal health.
Understanding the Importance of Prenatal Supplements:
Prenatal supplements are critical to supporting the health and well-being of both mother and baby throughout the pregnancy. Supplementation is especially important for older mothers, who may lose key nutrients as they age. These supplements are intended to fill nutritional gaps by supplying vital vitamins and minerals required for proper fetal growth and maternal health.
Key Nutrients for Older Mothers:
- Folic Acid: Essential for neural tube development, folic acid helps prevent birth defects such as spina bifida and anencephaly. Older mothers may require higher doses of folic acid to mitigate the risk of these abnormalities.
- Iron: Adequate iron intake is vital for preventing maternal anemia and ensuring proper oxygen delivery to the fetus. Older mothers are more susceptible to iron deficiency due to factors such as decreased absorption rates and preexisting health conditions.
- Calcium and Vitamin D: These nutrients are crucial for bone health and fetal skeletal development. Older mothers may need additional calcium and vitamin D supplementation to support both their own bone density and the growing needs of the fetus.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) is a type of omega-3 fatty acid essential for brain and eye development in the fetus. Older mothers can benefit from omega-3 supplementation to support cognitive development and reduce the risk of preterm birth.
- Vitamin B12: Older mothers may have reduced absorption of vitamin B12, which is important for neurological function and red blood cell formation. Supplementing with vitamin B12 can help prevent deficiencies and support maternal energy levels.
The Impact of Advanced Maternal Age:
Advanced maternal age is associated with a variety of physiological changes and potential problems. Older moms are more likely to have gestational diabetes, hypertension, and chromosomal abnormalities like Down syndrome. Furthermore, fertility falls with age, making conception more difficult and raising the risk of pregnancy-related disorders. Prenatal supplements are a proactive method to address these concerns and improve mother and fetal outcomes.
Choosing the Right Prenatal Supplement:

When choosing a prenatal vitamin, consider dosage, formulation, and quality. Older women may benefit from prenatal vitamins that are specifically designed for their requirements, with increased concentrations of critical minerals like folic acid, iron, and calcium. Consult with a healthcare expert to identify the best supplement program for your specific health status and nutritional needs.
Finally, prenatal supplements are essential for older women’ health and well-being during pregnancy. These supplements assist reduce the hazards associated with advanced maternal age and improve pregnancy outcomes by supplying important nutrients required for fetal growth and maternal health. With informed supplementation and complete prenatal care, older mothers can confidently begin their pregnant journey, assuring the greatest possible start for themselves and their babies.