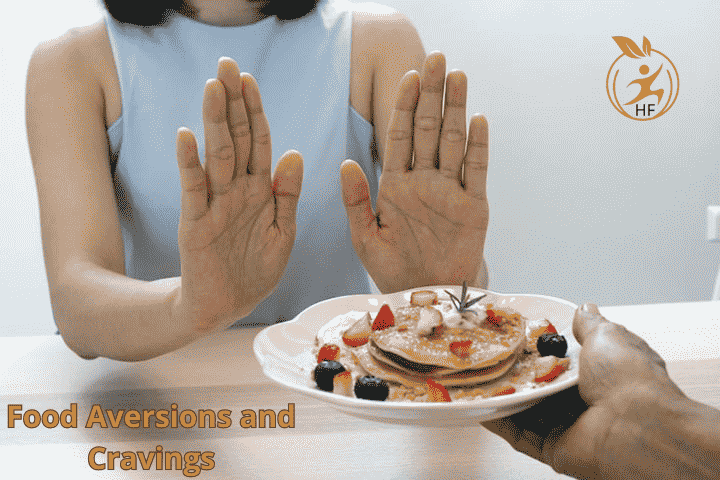
Embarking on the journey of pregnancy is an experience marked by an array of physical and emotional transformations. This voyage is no exception for women who find themselves conceiving later in life. Termed geriatric pregnancy, it encapsulates the profound journey of motherhood for women aged 35 and beyond. Amidst the unique joys and challenges this journey presents, one significant aspect often navigated with care and consideration is the realm of food aversions and cravings.
Navigating food aversions and cravings becomes particularly crucial during geriatric pregnancy, where maternal well-being and nutrition stand at the forefront of concern. These physiological shifts not only impact the expecting mother’s dietary habits but also hold implications for the overall health and development of the unborn child.
In this comprehensive exploration, we delve deep into the nuances of managing food aversions and cravings during geriatric pregnancy. Through insightful discussions and practical strategies, we aim to empower expecting mothers and their healthcare providers with the knowledge and tools necessary to navigate this pivotal aspect of maternal care. Join us as we embark on this journey, uncovering the intricacies of nurturing both body and soul amidst the tapestry of geriatric pregnancy.
Understanding Geriatric Pregnancy:
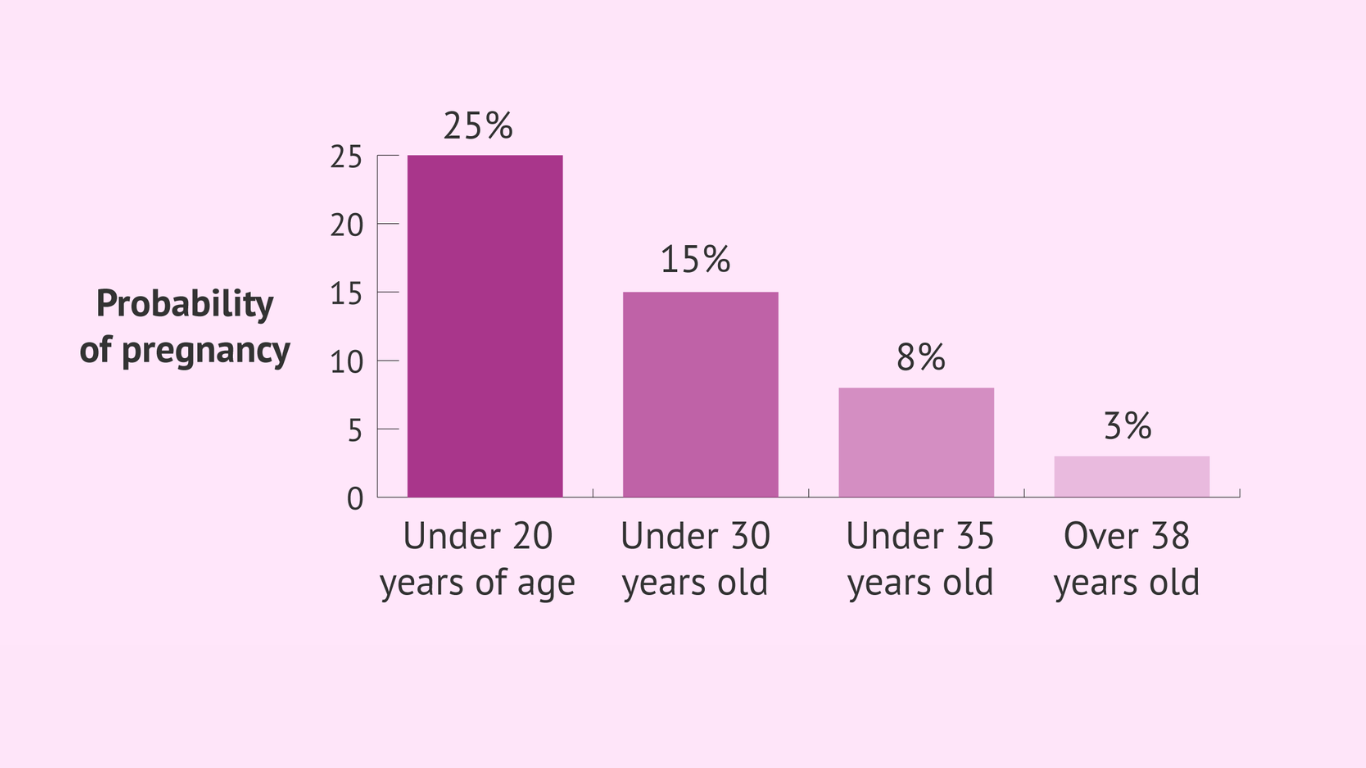
The term “geriatric pregnancy” may sound alarming, but it simply refers to pregnancies in women aged 35 and older. While advancements in healthcare have made it increasingly common for women to delay childbearing for various reasons such as career, education, or personal circumstances, it’s essential to recognize that pregnancy at an older age may entail additional risks and considerations. These risks can include higher rates of chromosomal abnormalities, gestational diabetes, hypertension, and complications during childbirth.
Impact of Food Aversions and Cravings:
Food aversions and cravings are hallmark features of pregnancy, affecting the majority of expectant mothers to some degree. However, in geriatric pregnancy, these phenomena can be particularly pronounced and may pose unique challenges. Food aversions, characterized by an intense dislike or avoidance of certain foods, can disrupt maternal nutrition by limiting the variety of foods consumed. On the other hand, cravings, often for specific types of foods or flavors, can lead to excessive calorie intake or unhealthy dietary choices if not managed appropriately.
Causes of Food Aversions and Cravings:
It is unclear what causes dietary aversions and appetites throughout pregnancy, including geriatric pregnancy. However, hormonal oscillations, particularly changes in estrogen and progesterone levels, are thought to play an important effect. Furthermore, increased perceptions of smell and taste, as well as psychological and cultural influences, can all contribute to the formation and exacerbation of food aversions and desires.
Managing Food Aversions:
Managing food aversions during geriatric pregnancy requires a proactive and flexible approach. Here are some strategies that expectant mothers can consider:
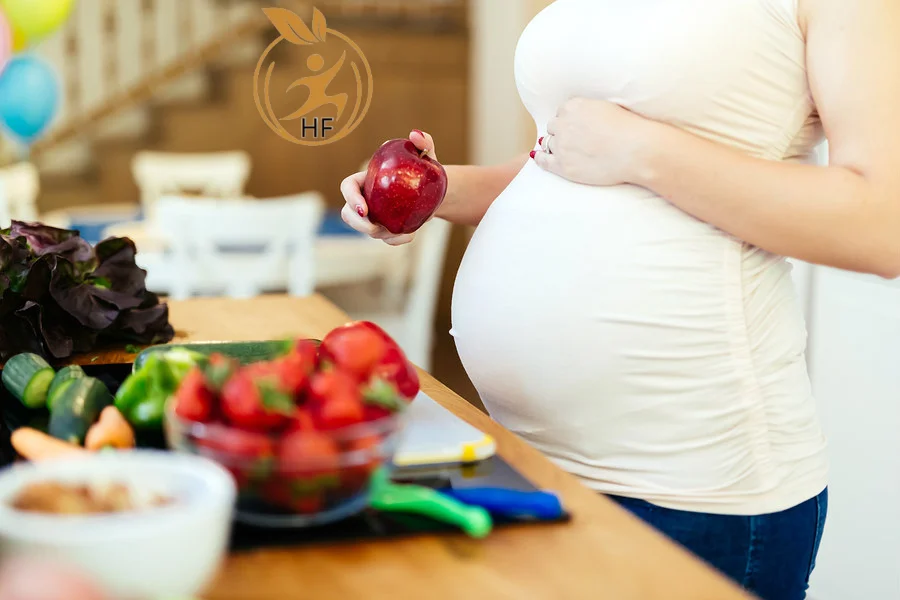

- Experiment with Different Foods: If certain foods trigger aversions, explore alternative options that provide similar nutritional benefits. For example, if meat is off-putting, try incorporating plant-based protein sources such as legumes, tofu, or quinoa into your diet.
- Focus on Nutrient-Rich Foods: Prioritize consuming nutrient-dense foods that support maternal and fetal health, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and dairy or dairy alternatives. Incorporating a variety of colors, flavors, and textures can make meals more appealing.
- Modify Cooking Methods: Altering the way foods are prepared can sometimes mitigate aversions. For instance, if the smell of certain foods cooking is bothersome, opt for blander cooking methods like steaming or baking instead of frying or grilling.
- Eat Small, Frequent Meals: Instead of large meals that may be overwhelming, try eating smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day. This approach can help prevent hunger-induced nausea and make it easier to consume adequate nutrients.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water is essential during pregnancy, especially if nausea or vomiting is a concern. Sipping on water throughout the day and opting for hydrating foods like fruits and vegetables can help maintain hydration levels.
- Consider Prenatal Supplements: If food aversions make it difficult to obtain essential nutrients from diet alone, talk to your healthcare provider about the possibility of taking prenatal supplements to fill nutritional gaps.
Managing Food Cravings:
While food cravings can be enjoyable, they can also pose challenges if they lead to excessive consumption of unhealthy foods. Here are some tips for managing food cravings during geriatric pregnancy:
- Practice Moderation: It’s okay to indulge in cravings occasionally, but aim for moderation to prevent excessive calorie intake and weight gain. Instead of denying cravings entirely, consider incorporating small portions of desired foods into balanced meals and snacks.
- Opt for Healthier Alternatives: If craving sweets, for example, choose healthier options such as fresh fruits, yogurt with honey, or dark chocolate in moderation. Similarly, if craving salty or savory foods, opt for whole-grain crackers with hummus, nuts, or air-popped popcorn instead of processed snacks.
- Identify Triggers: Pay attention to the circumstances or emotions that trigger cravings. Stress, fatigue, boredom, or specific environmental cues can all influence cravings. Finding alternative ways to address these triggers, such as practicing relaxation techniques or engaging in enjoyable activities, can help reduce the intensity of cravings.
- Plan Ahead: Stocking your kitchen with nutritious snacks and meal options can help prevent impulsive choices driven by cravings. Having pre-prepared healthy snacks readily available can make it easier to resist less nutritious options when cravings strike.
- Seek Support: Share your experiences and challenges with food cravings with your healthcare provider, partner, or support network. Having understanding and encouragement from others can make it easier to navigate cravings and stay on track with your dietary goals.
Navigating food aversions and cravings during geriatric pregnancy requires patience, flexibility, and proactive management. By understanding the underlying causes of these phenomena and implementing strategies to address them, expectant mothers can support their nutritional needs and promote a healthy pregnancy outcome. Additionally, maintaining open communication with healthcare providers and seeking support from loved ones can enhance the overall pregnancy experience. Remember that every pregnancy is unique, and it’s essential to prioritize self-care and well-being throughout this transformative journey.