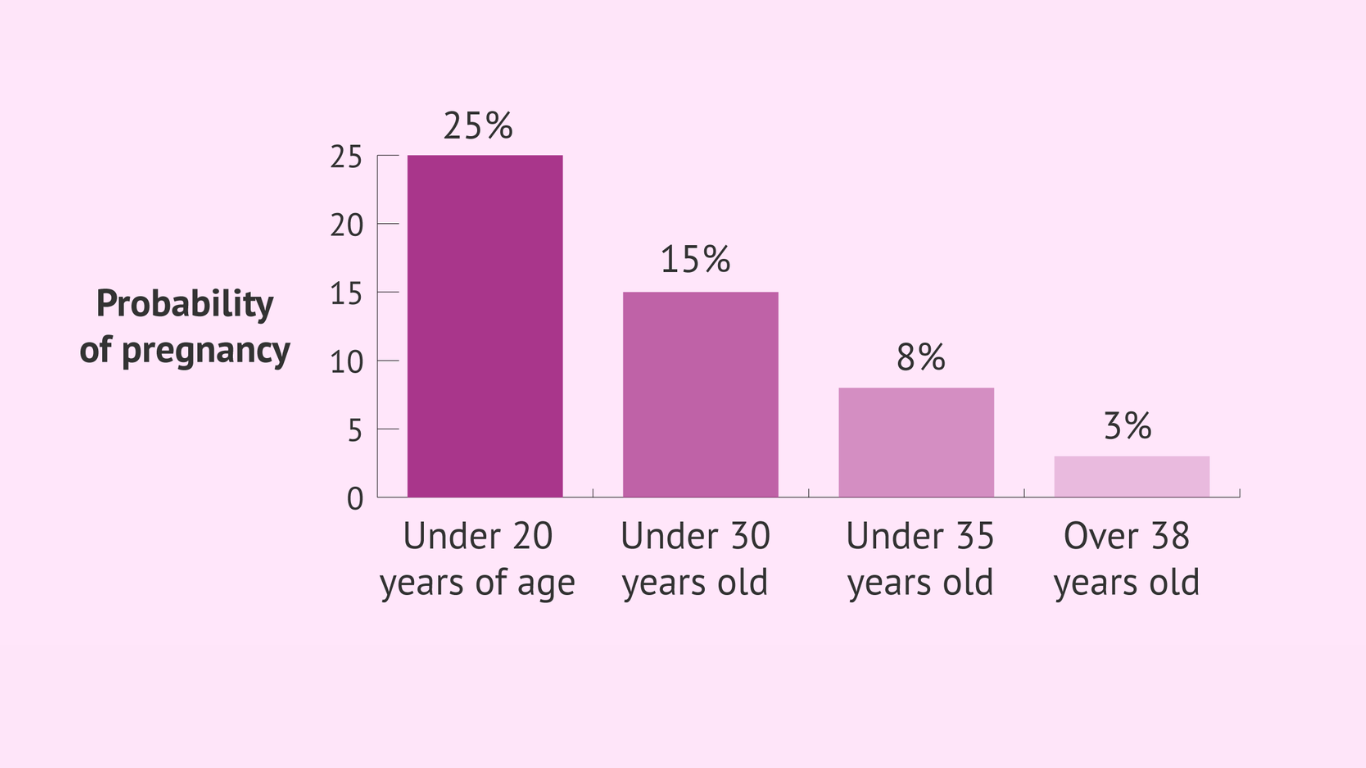
Gestational diabetes, a disorder marked by elevated blood sugar levels during pregnancy, can provide unique problems, particularly for older mothers-to-be. Women are delaying pregnancy to seek careers, achieve financial security, or for personal reasons, and the incidence of gestational diabetes in older pregnancies is increasing. However, with correct management and understanding, older expecting mothers can successfully navigate this illness and ensure a healthy pregnancy for themselves and their babies. This comprehensive guide will delve into the complexities of managing gestational diabetes in later pregnancies, covering everything from risk factors to dietary concerns and medicinal therapies.
Understanding Gestational Diabetes:

Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is defined as diabetes diagnosed for the first time during pregnancy. Older pregnancies are more likely to develop GDM due to age-related variables such as lower insulin sensitivity and pancreatic function. Other risk factors, like as obesity, a family history of diabetes, and certain ethnicities, can also increase the likelihood of developing gestational diabetes.
Importance of Early Screening:
For older pregnant women, early detection of gestational diabetes is critical. Healthcare practitioners normally recommend screening between 24 and 28 weeks of gestation, however for older expecting moms, screening may be done earlier. Early detection enables timely care, lowering the risk of problems for both mother and infant.
Dietary Management:
A well-balanced diet is essential for managing gestational diabetes. Older pregnant women should collaborate closely with qualified dietitians to create meal programs that control blood sugar levels while also delivering critical nutrients for maternal and fetal health. Emphasizing whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, and vegetables while restricting simple sugars and refined carbohydrates can help to keep blood glucose levels stable.
Regular Physical Activity:
Physical activity benefits all pregnant women, even those with gestational diabetes. However, older expecting moms should approach exercise with caution, taking into account their age and any underlying health concerns. Low-impact exercises like walking, swimming, and prenatal yoga help boost insulin sensitivity and general well-being throughout pregnancy.
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels:
Blood glucose levels must be monitored often in order to manage gestational diabetes effectively. Because of age-related metabolic changes, older pregnant women may require more frequent monitoring. Healthcare experts frequently urge that patients self-monitor their blood glucose levels numerous times each day in order to observe patterns and adapt medication accordingly.
Medical Interventions:
In rare circumstances, dietary and lifestyle adjustments may not be adequate to manage gestational diabetes in older pregnancies. To assist control blood sugar levels, doctors may give insulin or oral medicines. Expectant moms must follow their treatment programs and attend regular prenatal checkups to ensure maternal and fetal well-being.
Potential Complications:
While good management considerably reduces the risk, gestational diabetes in older pregnancies can still result in problems such as hypertension, macrosomia (high birth weight), and cesarean section. Close monitoring by healthcare professionals throughout the pregnancy can help to reduce these risks and provide the best possible outcomes for both mother and baby.
Managing gestational diabetes in later pregnancies necessitates a multimodal approach that includes dietary changes, regular physical activity, blood glucose monitoring, and medication therapies as needed. Working closely with healthcare specialists and adopting healthy lifestyle practices can help older pregnant mothers handle gestational diabetes efficiently, resulting in a safe and successful pregnancy. Remember, proactive treatment is essential for supporting maternal and fetal well-being and laying the groundwork for a joyful and meaningful transition to motherhood.